Thermodynamic Properties and Data
| Description |
Equations |
| Mechanical equilibrium |
Psys=Psurr |
| Thermal equilibrium |
Tsys=Tsurr |
| Chemical equilibrium |
μ(t1)=μ(t2) |
| Gibbs phase rule |
F=2+c−p−r |
| Quality |
x=nl+nvnv=vv−vlv−vl |
| Critical point |
(∂v∂P)Tc=0,(∂v2∂2P)Tc=0 |
| System Type |
Equations |
| Closed systems |
Δu+ΔeK+ΔeP=q+w |
| Closed systems |
Δu=q+w |
| Open systems |
dtdU=in∑n˙ihi+out∑n˙ihi+Q˙+W˙s |
| Open system at steady state |
0=in∑n˙ihi+out∑n˙ihi+Q˙+W˙s |
| Description |
Equations |
| Work |
w=−∫Pextdv |
| Enthalpy |
h=u+Pv |
| Efficiency of irreversible isothermal expansion |
η=wrevwirrev |
| Efficiency of irreversible isothermal compression |
η=wirrevwrev |
| Description |
Equations |
| Constant volume heat capacity |
cv=(∂T∂u)v |
| Constant pressure heat capacity |
cP=(∂T∂h)P |
| Ideal gas heat capacity |
cP=cv+R |
| Condensed phase heat capacity (l, s) |
cP≈cv |
| Mean heat capacity of gas |
cˉP=T2−T11∫T1T2cP(T)dT |
| Description |
Equations |
| Enthalpy of vaporization |
Δhvap=hv−hl |
| Enthalpy of fusion |
Δhfus=hs−hl |
| Enthalpy of sublimation |
Δhsub=hv−hs |
| Enthalpy of phase change at any T |
Δhvap(T)=Δhvap(Tb)+∫TbT(cPv−cPl)dT |
| Enthalpy of reaction |
Δhrxn∘=∑νiΔhf,i |
| System Type |
Equations |
| Isolated system |
ΔSuniv≥0 |
| Closed system |
ΔSsys−TsurrQsys≥0 |
| Open system |
out∑n˙isi−in∑n˙isi−TsurrQ˙+dtdS≥0 |
| Open system at steady state |
out∑n˙isi−in∑n˙isi−TsurrQ˙≥0 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Entropy |
ds=Tδqrev |
| Description |
γ |
Equation |
| Polytropic |
- |
PVγ=const |
| Isobaric |
0 |
P=const |
| Isothermal |
1 |
PV=const |
| Isentropic |
k=cvcP |
PVk=const |
| Isochoric |
∞ |
V=const |
Isoenergetic process (Δu=0⟹ΔT=0) of ideal gas has similar analysis.
| Description |
Equations |
Condition
★ Ideal gas |
ΔT=0 |
| Internal energy change |
Δu=0 |
| Enthalpy change |
Δh=0 |
| First law |
Δu=q+w=0 |
| Work (changing volume) |
w=−∫vRTdv=−RTln(v1v2) |
| Work (changing pressure) |
w=∫PRTdP=RTln(P1P2) |
| Heat |
q=−w |
| Entropy change |
Δs=∫Tδq=Tq=−Tw |
| Entropy change (changing volume) |
Δs=Rln(v1v2) |
| Entropy change (changing concentration) |
Δs=−Rln(c1c2) |
| Entropy change (changing pressure) |
Δs=−Rln(P1P2) |
| Description |
Equations |
Condition
★ Ideal gas |
q=0 |
| First law |
Δu=w |
| Enthalpy change |
Δh=Δu+RΔT |
| Work (changing volume) |
w=−∫vRTdv=−RTln(v1v2) |
| Work (changing pressure) |
w=∫PRTdP=RTln(P1P2) |
| Entropy change |
Δs=0 |
| Heat capacity ratio |
γ=cvcP |
| PVT relationship |
P1V1γ=P2V2γT1V1γ−1=T2V2γ−1P1(1/γ)−1T1=P2(1/γ)−1T2 |
| Description |
Equations |
Condition
★ Ideal gas |
Δv=0 |
| Work |
w=0 |
| Internal energy change |
Δu=∫cv dT |
| First law |
q=Δu |
| Entropy change |
Δs=∫Tδq=∫Tdu=∫Tcv dT |
| Description |
Equations |
Condition
★ Ideal gas |
ΔP=0 |
| Internal energy change |
Δu=∫cv dT |
| Enthalpy change |
Δh=∫cp dT |
| Work |
w=−PΔv |
| Heat |
q=Δh |
| Entropy change |
Δs=∫Tδq=∫Tdh=∫Tcp dT |
| Description |
Equations |
| Net work |
−Wnet=∣W12∣+∣W23∣−∣W34∣−∣W41∣ |
| Net work and heat |
−Wnet=∣QH∣−∣QC∣ |
| Carnot efficiency |
η=1−TCTH |
| State properties after cycle |
Δucycle=0Δhcycle=0Δscycle=0 |
| Entropy change of surrounding |
Δssurr=0=−THqH−TCqC |
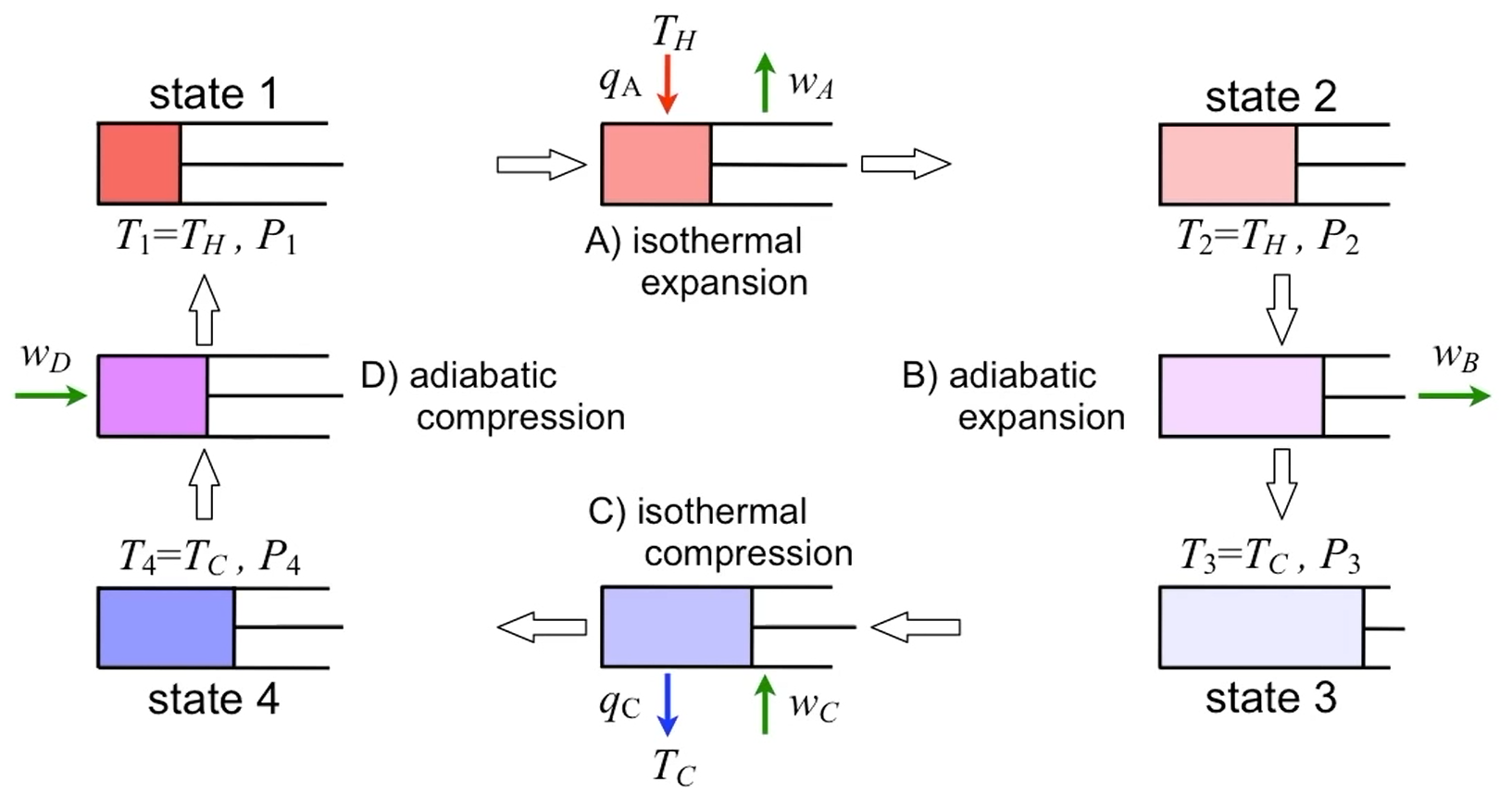
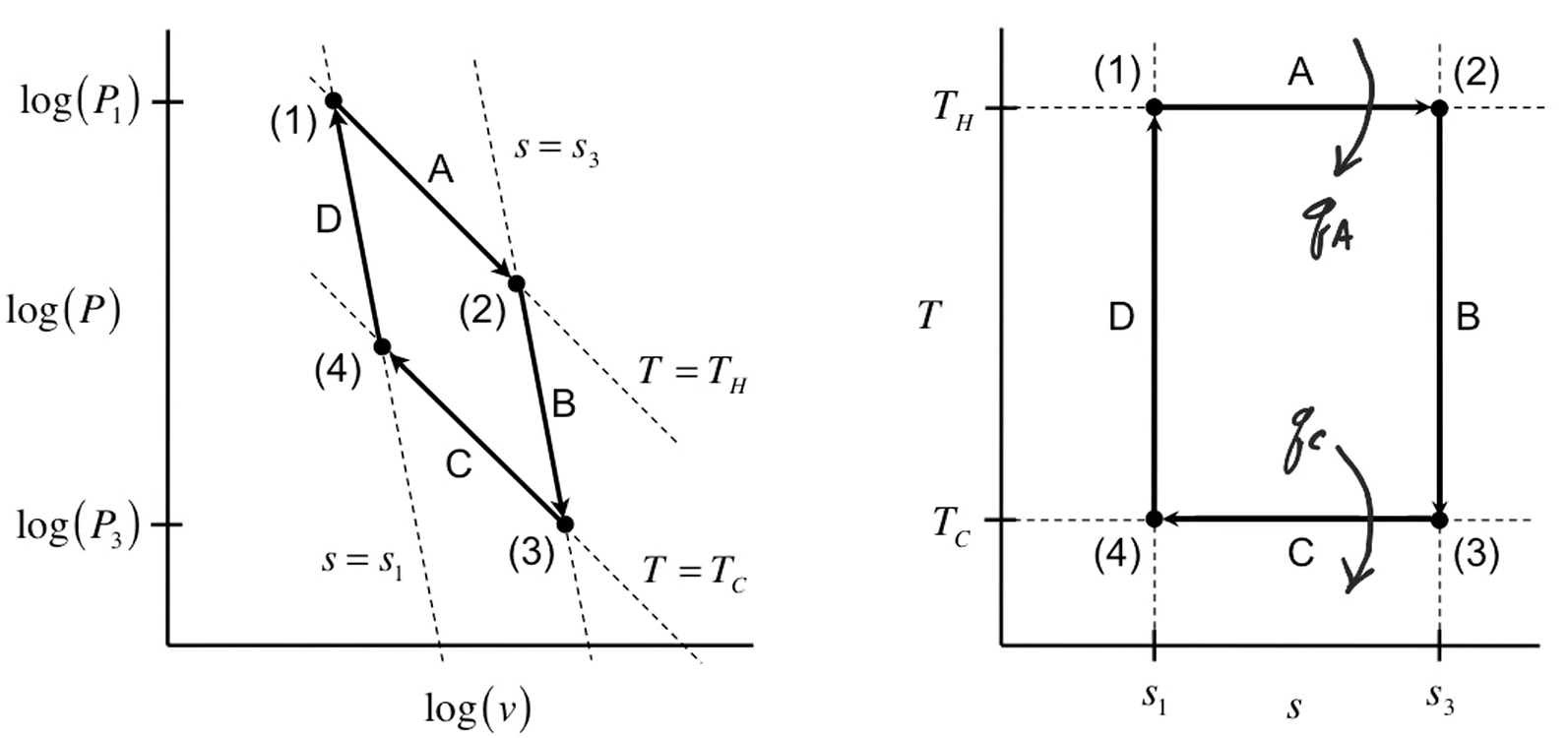
 Carnot cycle. (Episode C1 - Process Efficiency by Stu Adler UW)
Carnot cycle. (Episode C1 - Process Efficiency by Stu Adler UW)
 Carnot cycle diagrams. (Episode C1 - Process Efficiency by Stu Adler UW)
Carnot cycle diagrams. (Episode C1 - Process Efficiency by Stu Adler UW)
| Description |
Equations |
| Open system balance |
0=m˙1(h^+21v2+gz)1−m˙2(h^+21v2+gz)2 |
| Shaft work |
w˙s=∫v dP+Δe˙K+Δe˙P |
| Nozzle, diffuser simplifications |
0=ΔEP=Q˙=W˙s |
| Turbine, pump, compressor simplifications |
0=ΔEK=Q˙ |
| Heat exchanger simplifications |
0=ΔEP=ΔEK=W˙s |
| Throttling device simplifications |
0=ΔEP=ΔEK=Q˙=W˙s |
| Description |
Equations |
| Turbine |
w˙s=h2−h1q˙=0 |
| Condenser |
q˙=h3−h2w˙s=0 |
| Compressor |
w˙c=h4−h3=vΔPq˙=0 |
| Boiler |
q˙=h1−h4w˙s=0 |
| Efficiency |
η=q˙h∣w˙s∣−w˙c=h1−h4∣h2−h1∣−(h4−h3) |
| Net work |
w˙net=q˙H−∣q˙C∣=∣w˙s∣−w˙c |
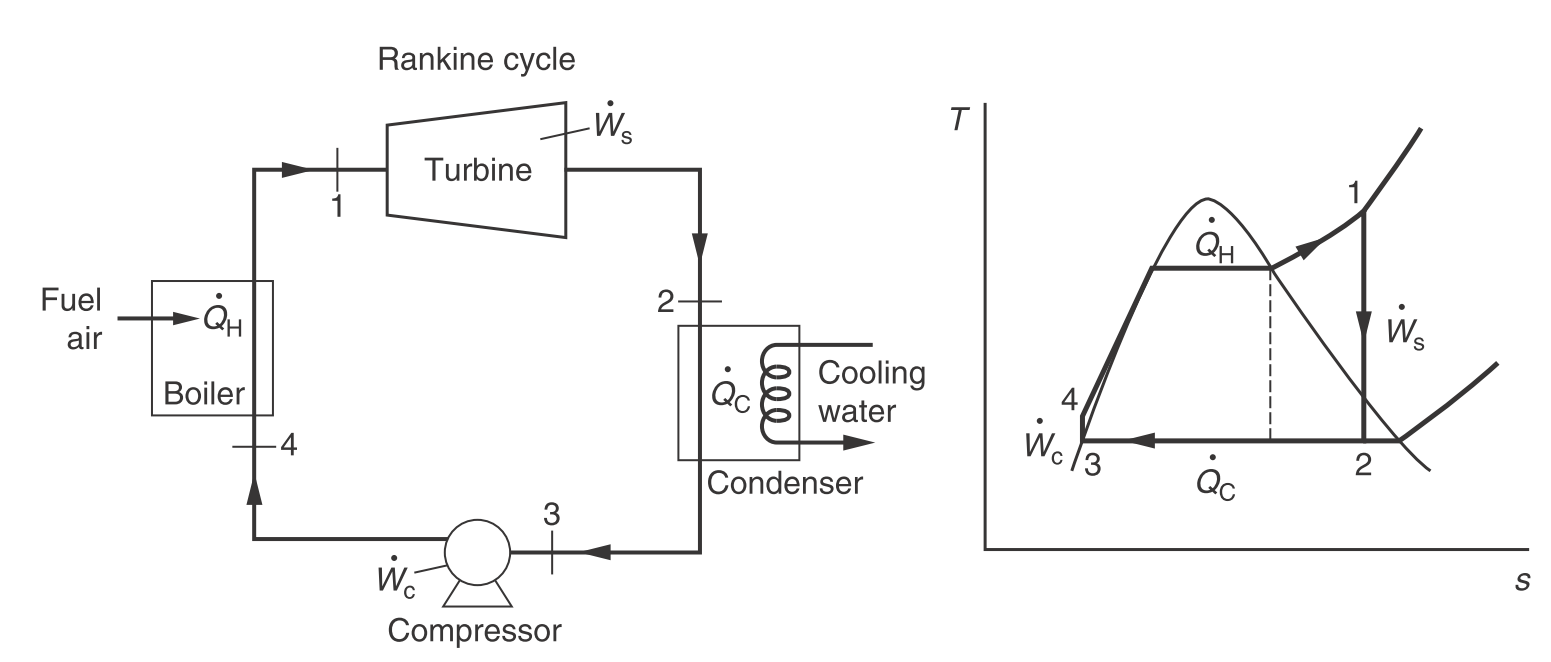
 Ideal Rankine cycle. (Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics 2e by Koretsky p164.)
Ideal Rankine cycle. (Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics 2e by Koretsky p164.)
| Description |
Equations |
| Evaporator |
q˙=h2−h1w˙s=0 |
| Compressor |
w˙s=h3−h2q˙=0 |
| Condenser |
q˙=h4−h3w˙s=0 |
| Value |
w˙s=0q˙=0Δh=0Δs>0 (irreversible expansion) |
| Coefficient of performance |
COP=W˙cQ˙C=h3−h2h2−h1 |
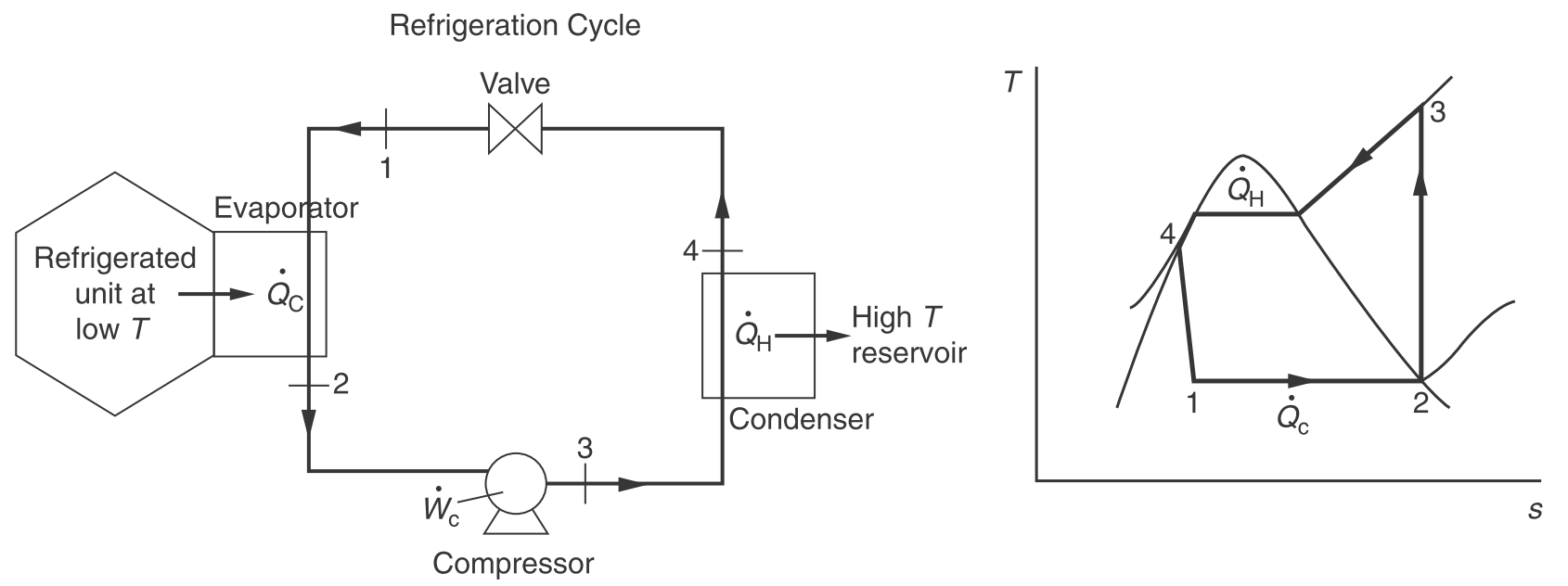
 Ideal refrigeration cycle. (Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics 2e by Koretsky p170.)
Ideal refrigeration cycle. (Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics 2e by Koretsky p170.)
| Description |
Equations |
| Conservative force |
Fij=−∇Γij |
| Potential |
Γij=−∫Fij dr |
| Description |
Equations (SI unit) |
Coulomb interaction
(electrostatic, point charges) |
Γij(r)=4πε0QiQjr1 |
Dipole-dipole interaction
(polar, electric dipole, Keesom) |
Γij(r)=−3(2)(4πε0)2μi2μj2kT1r61 |
Dipole-induced dipole interaction
(induction, Debye) |
Γij(r)=−(4πε0)2αiμj2r61 |
Induced dipole-induced dipole interaction
(dispersion, London) |
Γij(r)=−23(4πε0)2αiαjIi+IjIiIjr61 |
| Description |
Equations (SI unit) |
| van der Waals interaction |
Γijvdw=ΓijK+ΓijD+ΓijL=−r6Cvdw |
| Keesom coefficient |
CK=3(2)(4πε0)2μi2μj2kT1 |
| Debye coefficient |
CD=(4πε0)2αiμj2+αjμi2 |
| London coefficient |
CL=23(4πε0)2αiαjIi+IjIiIj |
| Description |
Equations (CGS unit) |
Coulomb interaction
(electrostatic, point charges) |
Γij(r)=rQiQj |
Dipole-dipole interaction
(polar, electric dipole, Keesom) |
Γij(r)=−3(2)kTμi2μj2r61 |
Dipole-induced dipole interaction
(induction, Debye) |
Γij(r)=−r6αiμj2 |
Induced dipole-induced dipole interaction
(dispersion, London) |
Γij(r)=−23r6αiαjIi+IjIiIj |
| Description |
Equations (CGS unit) |
| van der Waals interaction |
Γijvdw=ΓijK+ΓijD+ΓijL=−r6Cvdw |
| Keesom coefficient |
CK=3(2)kTμi2μj2 |
| Debye coefficient |
CD=αiμj2+αjμi2 |
| London coefficient |
CL=23αiαjIi+IjIiIj |
| Description |
Equations (SI unit) |
| Hard sphere model |
Γ={0∞r>σr≤σ |
| Surtherland model |
Γ=⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧−r6Cvdw∞r>σr≤σ |
| Lennard-Jones potential |
Γ=r12Crep−r6Cvdw |
| Lennard-Jones potential |
Γ=4ε[(rσ)12−(rσ)6] |
| Description |
Equations |
| Ideal gas law |
Pv=RT |
| Compressibility factor |
z=RTPv |
| Reduced temperature |
Tr=TcT |
| Reduced pressure |
Pr=PcP |
| Pitzer acentric factor |
ω=−1−log10[Prsat(Tr=0.7)] |
| Generalized compressibility |
z=z(0)+ωz(1) |
| Description |
Equations |
van der Waals EOS
(pressure explicit form) |
P=v−bRT−v2a |
van der Waals EOS
(cubic form) |
Pv3−(RT+Pb)v2+av−ab=0 |
van der Waals EOS
(reduced form) |
P=3vr−18Tr−vr23 |
| Intermolecular force (pressure) correction |
a=6427Pc(RTc)2 |
| Volume correction |
b=8PcRTc |
| Critical compressibility factor |
zc=83 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Redlich-Kwong EOS |
P=v−bRT−Tv(v+b)a |
| Intermolecular force (pressure) correction |
a=0.42748PcR2Tc2.5 |
| Volume correction |
b=0.08664PcRTc |
| Critical compressibility factor |
zc=31 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Peng-Robinson EOS |
P=v−bRT−v(v+b)+b(v−b)aα(T) |
| Intermolecular force (pressure) correction |
a=0.45724PcR2Tc2 |
| Volume correction |
b=0.07780PcRTc |
| Constant |
α(T)=[1+κ(1−Tr)]2 |
| Constant |
κ=0.37464+1.54226ω−0.26992ω2 |
| Critical compressibility factor |
zc=0.307 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Virial EOS |
z=RTPv=1+vB+v2C+v3D+⋯ |
| Second virial coefficient |
B=PcRTcBr |
| Reduced second virial coefficient |
Br=B(0)+ωB(1) |
| 0th order correction |
B(0)=0.083−Tr1.60.422 |
| 1st order correction |
B(1)=0.139−Tr4.20.172 |
| Description |
Equations |
| a for binary mixtures |
amix=y12a1+2y1y2a12+y22a2 |
| a of different species interaction |
a12=a1a2(1−k12) |
| b for binary mixtures |
bmix=y1b1+y2b2 |
| a for multicomponent mixtures |
amix=i∑j∑yiyjaij |
| b for multicomponent mixtures |
bmix=i∑yibi |
| Description |
Equations |
| Second virial coefficient for binary mixture |
Bmix=y12B11+2y1y2B12+y22B22 |
| Second virial coefficient for multicomponent mixture |
Bmix=i∑j∑yiyjBij |
| Third virial coefficient for multicomponent mixture |
Cmix=i∑j∑k∑yiyjykCijk |
| Description |
Equations |
| Pseudocritical temperature |
Tpc=∑yiTc,i |
| Pseudocritical pressure |
Ppc=∑yiPc,i |
| Pseudocritical acentric factor |
ωpc=∑yiωc,i |
EOS for liquids and solids
| Description |
Equations |
| Thermal expansion coefficient |
β=v1(∂T∂v)P |
| Isothermal compressibility |
κ=−v1(∂P∂v)T |
| Rackett equation |
vlsat=PcRTc(0.29056−0.08775ω)(1+(1−Tr)2/7) |
| Description |
Equations |
| Total differential |
dz=(∂x∂z)ydx+(∂y∂z)xdy |
Clairaut’s theorem
Symmetry of second derivative |
∂x∂(∂y∂z)=∂y∂(∂x∂z) |
| Chain rule |
∂x∂z=∂y∂z∂x∂y |
Cyclic relation
Triple chain rule |
(∂y∂x)z(∂z∂y)x(∂x∂z)y=−1 |
| Relations |
Internal energy u |
Enthalpy h |
Helmholz energy a |
Gibbs energy g |
| Definition |
- |
h=u+Pv |
a=u−Ts |
g=h−Ts |
| Fundamental property relations |
du=Tds−Pdv |
dh=Tds+vdP |
da=−sdT−Pdv |
dg=−sdT+vdP |
| Fundamental grouping |
{u,s,v} |
{h,s,P} |
{a,T,v} |
{g,T,P} |
| Fundamental grouping relations |
(∂s∂u)v=T |
(∂s∂h)P=T |
(∂T∂a)v=−s |
(∂T∂g)P=−s |
| Fundamental grouping relations |
(∂v∂u)s=−P |
(∂P∂h)s=v |
(∂v∂a)T=−P |
(∂P∂g)T=v |
| Maxwell’s relations |
(∂v∂T)s=−(∂s∂P)v |
(∂P∂T)s=(∂s∂v)P |
(∂v∂s)T=(∂T∂P)v |
(∂P∂s)T=−(∂T∂v)P |
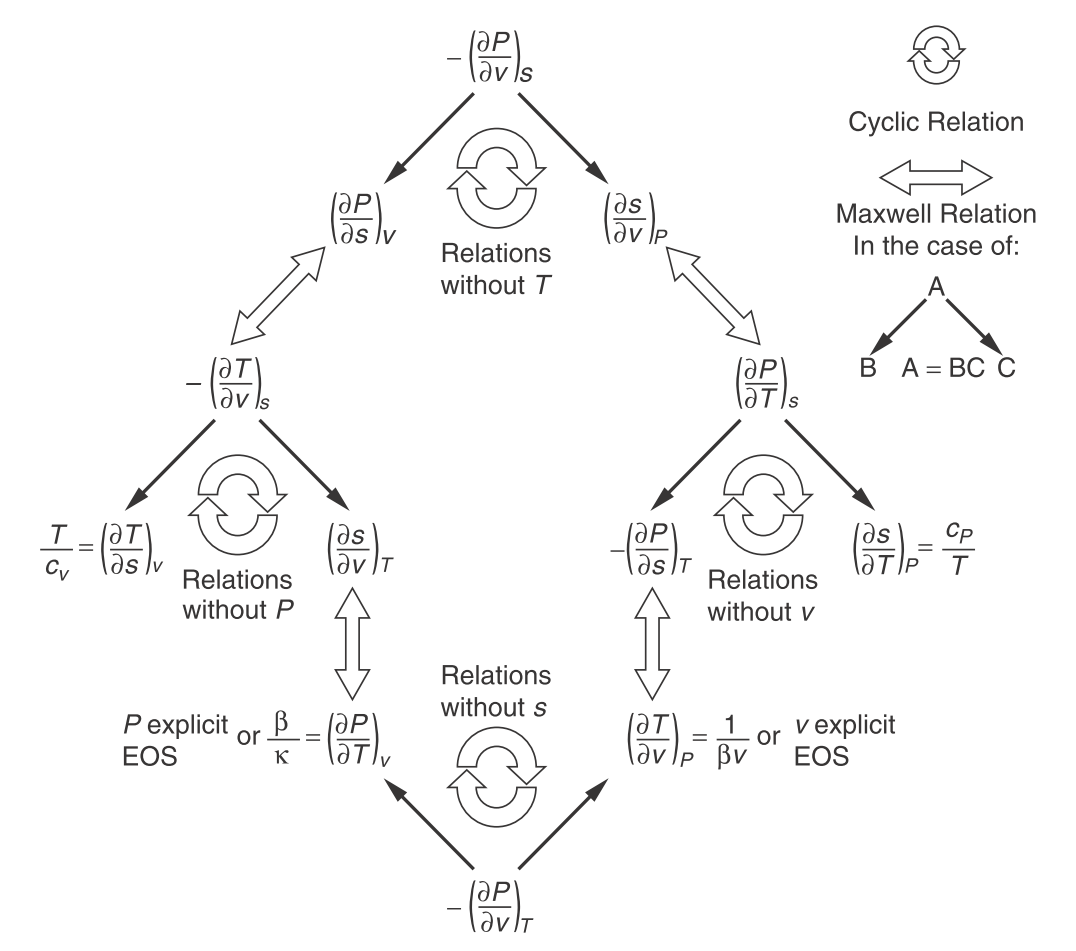
 Thermodynamic relations. (Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics 2e by Koretsky p274.)
Thermodynamic relations. (Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics 2e by Koretsky p274.)
| Description |
Equations |
| Constant volume heat capacity |
cv=(∂T∂u)v=T(∂T∂s)v |
| Constant pressure heat capacity |
cP=(∂T∂h)P=T(∂T∂s)P |
| Constant volume heat capacity of real gas |
cvreal=cvideal+∫videalvreal[T(∂T2∂2P)v]dv |
| Constant pressure heat capacity of real gas |
cPreal=cPideal−∫PidealPreal[T(∂T2∂2v)P]dP |
| Thermal expansion coefficient |
β=v1(∂T∂v)P |
| Thermal expansion coefficient of ideal gas |
β=T1 |
| Isothermal compressibility |
κ=−v1(∂P∂v)T |
| Isothermal compressibility of ideal gas |
κ=P1 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Entropy change s(T,v) |
ds=TcvdT+(∂T∂P)vdv |
| Entropy change s(T,P) |
ds=TcPdT+(∂T∂v)PdP |
| Internal energy change u(T,v) |
du=cvdT+[T(∂T∂P)v−P]dv |
| Enthalpy change h(T,P) |
dh=cPdT+[−T(∂T∂v)P+v]dP |
| General f(T,P) |
Ideal gas β=T1,κ=P1 |
| ds=TcPdT−βv dP |
ds=TcPdT−PRdP |
| dv=βv dT−κv dP |
dv=TvdT−PvdP |
| du=(cP−βPv)dT+(κPv−βvT)dP |
du=(cP−R)dT |
| dh=(cP−βPv)dT+v dP |
dh=cP dT |
| da=−s dT+(κPv−βvT)dP |
da=−s dT |
| dg=−s dT+v dP |
dg=−s dT+v dP |
| Description |
Equations |
| General departure function |
dep=real−ideal |
| Enthalpy departure function |
Δhdep=hreal−hideal |
| Entropy departure function |
Δsdep=sreal−sideal |
| Dimensionless enthalpy departure function |
RTcΔhdep=Tr2∫0P[−Pr1(∂Tr∂z)P]dPr |
| Dimensionless entropy departure function |
RΔsdep=∫0P−[Prz−1+PrTr(∂Tr∂z)P]dPr |
| Dimensionless enthalpy departure function with Lee-Kesler EOS |
RTcΔhdep=[RTcΔhdep](0)+ω[RTcΔhdep](1) |
| Dimensionless entropy departure function with Lee-Kesler EOS |
RΔsdep=[RΔsdep](0)+ω[RΔsdep](1) |
| Description |
Equations |
Joule-Thomson expansion
Adiabatic reversible throttling |
q˙=0w˙s=0Δh=0 |
| Joule-Thomson coefficient |
μJT=(∂P∂T)h |
| Joule-Thomson coefficient |
μJT=cPreal[−T(∂T∂v)P+v] |
| Description |
Equations |
| Gibbs free energy |
g=h−Ts |
| Second law of thermodynamics |
dGi≤0 |
| Criteria for chemical equilibrium |
giα=giβ |
Clapeyron equation
General phase equilibrium |
dTdP=ΔvΔs=TΔvΔh |
Clausius-Clapeyron equation
★ Vapor-liquid equilibrium
★ Ideal gas, negligible liquid volume |
PsatdPsat=RT2ΔhvapdT |
Clausius-Clapeyron equation
★ Vapor-liquid equilibrium
★ Ideal gas, negligible liquid volume
★ Δhvap independent of T |
lnP1satP2sat=−RΔhvap(T21−T11) |
| Antoine’s equation |
lnPsat=A−C+TB |
| Description |
Equations |
| Extensive total solution (mixture) property |
K |
| Intensive total solution (mixture) property |
k=nK |
| Extensive pure species property |
Ki |
| Intensive pure species property |
ki=niKi |
| Partial molar property |
Ki=(∂ni∂K)T,P,nj=i |
| Limiting case of partial molar property |
xi→1limKi=kixi→0limKi=Ki∞ |
| Differential of extensive property |
dK=(∂T∂K)P,nidT+(∂P∂K)T,nidP+∑Kidni |
Relation between properties
★ Constant T, P |
K=∑niKik=∑xiKi |
Gibbs-Duhem equation
★ Constant T, P |
∑nidKi=0 |
Corollary of Gibbs-Duhem equation
★ Binary mixture |
x1dx1dK1+x2dx1dK2=0 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Extensive property change of mixing |
ΔKmix=K−∑nikiΔKmix=∑ni(Ki−ki) |
| Intensive property change of mixing |
Δkmix=k−∑xikiΔkmix=∑xi(Ki−ki) |
| Enthalpy of mixing |
Δhmix=∑xi(hi−hi) |
| Enthalpy of mixing |
Δhmix=n+1Δh~s=Δh~sx1 |
| Enthalpy of solution |
Δh~s=x1Δhmix=Δhmix(n+1) |
Entropy of mixing
★ Ideal gas, regular solution |
Δsmix=−R∑yilnyi |
| Partial molar property change of mixing |
ΔKmix,i=Ki−ki |
| Description |
Equations |
Partial molar volume of species 1
★ Virial EOS |
V1=PRT+(y12+2y1y2)B11+2y22B12−y22B22 |
Partial molar volume of species 2
★ Virial EOS |
V2=PRT−y12B11+2y12B12+(y22+2y1y2)B22 |
Volume change of mixing
★ Virial EOS |
Δvmix=y1y2(2B12−B11−B22) |
| Partial molar property |
Ki=ki+ΔKmix,i |
Graphical method
Slope is difference |
dx1dk=K1−K2 |
Graphical method
K2 is intercept |
k=x1dx1dk+K2 |
Graphical method
K2 explicit |
K2=k−x1dx1dk |
T and P dependence of Gi
| Description |
Equations |
| Partial molar Gibbs energy dependence on temperature |
(∂T∂Gi)P,ni=−Si |
| Partial molar Gibbs energy dependence on temperature (measurable) |
[∂T∂(TGi)]P,ni=−T2Hi |
| Partial molar Gibbs energy dependence on pressure |
(∂P∂Gi)T,ni=−Vi |
| Description |
Equations |
| Chemical potential |
μi=Gi=(∂ni∂G)T,P,nj=i |
| Criteria for chemical equilibrium |
μiα=μiβ |
| General multicomponent equilibrium |
Δ[−T2HidT−TVidP+T1[∂xi∂μi]T,Pdxi]=0 |
Vapor liquid equilibrium
★ Ideal gas |
−T2hivdT−RPdP+Rxivdxiv=−T2HildT−TVildP+T1[∂xi∂μil]T,Pdxi |
| Description |
Equations |
Definition of fugacity of pure species
★ Constant T |
gi−gi∘=RTln(fi∘fi)P→0limφi=1 |
Fugacity of pure species
★ Constant T |
fi=φiP |
| Fugacity coefficient of pure species |
φi=Pfi |
| Definition of fugacity of species i in mixture |
μi−μi∘=RTln(f^i∘f^i)P→0limφ^i=1 |
| Fugacity of species i in mixture |
f^i=yiPφ^i |
Fugacity coefficient of species i in mixture
★ Constant T |
φ^i=pif^i=yiPf^i |
| Criteria for chemical equilibrium |
f^iα=f^iβ |
| Description |
Equations |
Reference state
★ Ideal gas |
P∘=PlowT∘=Tsysf^i∘=P∘ |
Fugacity of pure species
★ Constant T |
fi=φiP |
| Fugacity coefficient of pure species |
φi=Pfi |
| Fugacity from experimental data |
fiv=P∘exp(RTgi−gi∘) |
| Fugacity coefficient from experimental data |
φi=PP∘exp(RTgi−gi∘) |
| Fugacity from EOS |
RTln(P∘fiv)=∫P∘Pvi dP |
| Fugacity coefficient from EOS |
φi=PP∘exp[RT1∫P∘Pvi dP] |
| Fugacity coefficient from vdW EOS |
lnφiv=−ln[RT(vi−b)P]+vi−bb−RTvi2a |
| Fugacity coefficient from virial form of vdW EOS |
lnφiv=(b−RTa)RTP |
| Fugacity coefficient from generalized correlations |
lnφiv=∫P∘P(zi−1)PdP |
| Generalized fugacity coefficient with Lee-Kesler EOS |
logφi=logφ(0)+ωlogφ(1) |
| Description |
Equations |
Reference state
★ Ideal gas |
P∘=PlowT∘=Tsysni∘=ni,sysfi∘=yiP∘V∘=P∘nRT |
Fugacity of species i in mixture
★ EOS
★ Full i-j interaction |
f^i=yiφ^iP |
Fugacity of species i in mixture
★ Lewis fugacity rule
★ Same species interaction only, i-i interaction |
f^i=yiφiPφ^i=φi |
Fugacity of species i in mixture
★ Ideal gas, no interaction |
f^i=yiPφ^i=1 |
Fugacity coefficient of species i in mixture
★ Constant T |
φ^i=pif^i=yiPf^i |
| Fugacity coefficient from v-explicit EOS |
φ^i=PP∘exp[RT1∫P∘PVi dP] |
| Fugacity coefficient from P-explicit EOS |
φ^i=PP∘exp[−RT1∫V∘VPi dV] |
| Description |
van der Waals EOS |
| Pure species i |
lnφi=vi−bibi−ln(RT(vi−bi)P)−RTvi2ai |
| Species 1 in a binary mixture |
lnφ^1=v−bb1−ln(RT(v−b)P)−RTv2(y1a1+y2a12) |
| Species i in a mixture |
lnφ^i=v−bbi−ln(RT(v−b)P)−RTv2k=1∑mykaik |
| Description |
Redlich-Kwong EOS |
| Pure species i |
lnφi=zi−1−ln(RT(vi−bi)P)−biRT1.5ailn(1+vibi) |
| Species 1 in a binary mixture |
lnφ^1=bb1(z−1)−ln(RT(v−b)P)+bRT1.51[bab1−2(y1a1+y2a12)]ln(1+vb) |
| Species i in a mixture |
lnφ^i=bbi(z−1)−ln(RT(v−b)P)+bRT1.51[babi−2k=1∑mykaik]ln(1+vb) |
| Description |
Peng-Robinson EOS |
| Pure species i |
lnφi=zi−1−ln(RT(vi−bi)P)−22biRT(aα)iln[vi+(1−2)bivi+(1+2)bi] |
| Species 1 in a binary mixture |
lnφ^1=bb1(z−1)−ln(RT(v−b)P)+22bRTaα[bb1−aα2(y1(aα)1+y2(aα)12)]ln[v+(1−2)bv+(1+2)b] |
| Species i in a mixture |
lnφ^i=bbi(z−1)−ln(RT(v−b)P)+22bRTaα[bbi−aα2k=1∑myk(aα)ik]ln[v+(1−2)bv+(1+2)b] |
| Description |
Equations |
| Interaction parameter a for multicomponent mixtures |
amix=∑∑yiyjaij |
| Like attractions |
aii=ai |
| Unlike attractions |
aij=aiiajj(1−kij) |
| Volume parameter a for multicomponent mixtures |
bmix=∑yibi |
| Description |
Equations |
| Volume change of mixing |
Δvmix=0 |
| Enthalpy change of mixing |
Δhmix=0 |
| Entropy change of mixing |
Δsmix=−R∑yilnyi>0 |
| Gibbs energy change of mixing |
Δgmix=RT∑yilnyi<0 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Reference state of fugacity in ideal solution |
f^i∘=xifi∘ |
Lewis/Randall rule reference state of fugacity
★ Solvent, pure limit
★ Same species (a-a) interaction only |
fi∘=fif^i∘=xifi |
Henry’s law reference state of fugacity
★ Solute, dilute limit
★ Different species (a-b) interaction only |
fi∘=Hif^i∘=xiHi |
Lewis/Randall rule
| Description |
Equations |
Lewis/Randall rule reference state of fugacity
★ Solvent, pure limit
★ Same species (a-a) interaction only |
fi∘=fif^i∘=xifi |
| Pure liquid fugacity with Poynting correction at T, P |
fil=φisatPisatexp[∫PisatPRTvildP] |
Pure liquid fugacity with Poynting correction at T, P
★ Incompressible liquid |
fil=φisatPisatexp[RTvil(P−Pisat)] |
Pure liquid fugacity
★ P≈Psat |
fil=φisatPisat |
Pure liquid fugacity
★ Ideal gas (low P, low sat P) |
fil=Pisat |
| Description |
Equations |
Henry’s law reference state of fugacity
★ Solute, dilute limit
★ Different species (a-b) interaction only |
fi∘=Hif^i∘=xiHi |
| Pressure dependence of Henry’s constant |
Hi(P)=Hi(P1)exp[∫P0PRTVi∞dP] |
| Temperature dependence of Henry’s constant |
Hi(T)=Hi(T1)exp[∫T0TRT2hiv−Hi∞dP] |
| Description |
Equations |
| Activity coefficient |
γi=f^i∘f^il=xifi∘f^il |
| Activity coefficient in Lewis/Randall rule reference state |
xi→0limγiLR=fiHixi→1limγiLR=1 |
| Activity coefficient in Henry’s law reference state |
xi→0limγiH=1xi→1limγiH=Hifi |
| Activity |
ai=fi∘f^ilai=xiγi |
Gibbs-Duhem Equation
★ Constant T, P |
∑xid(lnγi)=0 |
Corollary of Gibbs-Duhem equation
★ Binary mixture |
x1(∂x1∂lnγ1)T,P+x2(∂x2∂lnγ2)T,P=0 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Excess property |
kE=kreal−kideal |
| Excess property |
kE=Δkmixreal−Δkmixideal |
| Partial molar excess property |
KiE=Kireal−Kiideal |
| Excess Gibbs free energy |
gE=Δgmix−RT∑xilnxi |
| Excess Gibbs free energy |
gE=RT∑xilnγi |
| Partial molar excess Gibbs free energy |
GiE=RTlnγi |
Area test for thermodynamic consistency
★ Lewis/Randall reference state
★ Constant T, P |
∫01ln(γbγa)dxa=0 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Two-suffix Margules equation |
gE=Axaxb |
| Activity coefficient |
GiE=RTlnγiGaE=Axb2GbE=Axa2 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Three-suffix Margules equation |
gE=xaxb[A+B(xa−xb)] |
| Activity coefficient |
GiE=RTlnγiGaE=(A+3B)xb2−4Bxb3GbE=(A−3B)xa2+4Bxa3 |
| Three-suffix Margules equation |
gE=xaxb(Abaxa+Aabxb) |
| Activity coefficient |
GiE=RTlnγiGaE=xb2[Aab+2(Aba−Aab)xa]GbE=xa2[Aba+2(Aab−Aba)xb] |
| Description |
Equations |
| van Laar equation |
gE=xaxb(Axa+BxbAB) |
| Activity coefficient |
GiE=RTlnγiGaE=A(Axa+BxbBxb)2GbE=B(Axa+BxbAxa)2 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Wilson equation |
gE=−RT[xaln(xa+Λabxb)+xbln(xb+Λbaxa)] |
| Activity coefficient |
GiEGaEGbE=RTlnγi=−RT[ln(xa+Λabxb)+xb(xb+ΛbaxaΛba−xa+ΛabxbΛab)]=−RT[ln(xb+Λbaxa)+xa(xa+ΛabxbΛab−xb+ΛbaxaΛba)] |
| Wilson parameters |
Λab=vavbexp(−RTλab)Λba=vbvaexp(−RTλba) |
Non-random two-liquid model (NRTL)
| Description |
Equations |
| Non-random two-liquid model (NRTL) |
gE=RTxaxb[xa+xbGbaτbaGba+xb+xaGabτabGab] |
| Activity coefficient |
GiE=RTlnγiGaE=RTxb2[(xa+xbGba)2τbaGba2+(xb+xaGab)2τabGab]GbE=RTxa2[(xa+xbGba)2τbaGba+(xa+xbGab)2τabGab2] |
| NRTL parameters |
Gab=exp(−ατab)Gba=exp(−ατba) |
| Description |
Equations |
| Two-suffix Margules equation (ternary system) |
gE=Aabxaxb+Aacxaxc+Abcxbxc |
| Partial excess Gibbs energy of species a |
GaE=Aabxb2+Aacxc2+(Aab+Aac−Abc)xbxc |
| Partial excess Gibbs energy of species b |
GbE=Aabxa2+Abcxc2+(Aab+Abc−Aac)xaxc |
| Partial excess Gibbs energy of species c |
GcE=Aacxa2+Abcxb2+(Aac+Abc−Aab)xaxb |
| Two-suffix Margules equation (multicomponent system) |
gE=i∑j∑2Aijxixj |
| Two-suffix Margules parameter |
Aii=0Aij=Aji |
| Description |
Equations |
| Wilson equation |
lnγi=1−ln(j=1∑mxjΛij)−k=1∑mln(j=1∑mxjΛkj)xkΛki |
| Wilson parameter |
Λjj=1 |
Non-random two-liquid model (NRTL)
| Description |
Equations |
| Non-random two-liquid model (NRTL) |
lnγi=l=1∑mxlGlij=1∑mτjixjGji+j=1∑ml=1∑mxlGljxjGij⎝⎜⎜⎜⎛τij−l=1∑mxlGljk=1∑mτkjxkGkj⎠⎟⎟⎟⎞ |
| NRTL parameters |
lnGij=−αijτijτij=0Gij=1 |
| Description |
Equations |
| Universal quasi-chemical theory (UNIQUAC) |
lnγi=lnxiΦi∗+2zqilnΦi∗θi+li+xiΦi∗j=1∑mxjlj+qi′⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡1−j=1∑mθj′τji−j=1∑mk=1∑mθk′τkjθj′τij⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤ |
| UNIQUAC parameters |
li=2z(ri−qi)−(ri−1)τjk=exp(−Tajk)τkk=1Φi∗=j=1∑mxjrjxiriθi=j=1∑mxjqjxiqiθi′=j=1∑mxjqj′xiqi′ |
T and P dependence of gE
| Description |
Equations |
| Excess Gibbs energy dependence on pressure |
(∂P∂gE)T,ni=vE=Δvmix |
| Excess Gibbs energy dependence on temperature |
[∂T∂(TgE)]P,ni=−T2hE=−T2Δhmix |
Excess Gibbs energy dependence on temperature
★ Regular solution |
gE=RT∑xilnγi=constant |
Excess Gibbs energy dependence on temperature
★ Athermal solution |
TgE=R∑xilnγi=constant |
T and P dependence of γi
| Description |
Equations |
| Activity coefficient dependence on pressure |
(∂P∂lnγi)T,x=RTVi−vi |
| Activity coefficient dependence on temperature |
(∂T∂lnγi)P,x=−RT2Hi−hi |
| Description |
Equations |
| Activity coefficient of pure solids |
Γi=1 |
| Fugacity of pure solids |
f^is=fis |
Fugacity of solid solutions
★ Treat like liquid solution |
f^is=XiΓifis |
| Description |
Equations |
| General VLE condition |
f^ivyiφ^ivP=f^il=xiγilfi∘ |
| Description |
Equations |
Raoult’s law
★ Ideal gas φ^iv=1
★ Ideal solution γil=1
★ Lewis/Randall ref state fi∘=fi=Pisat |
yiP=xiPisat |
| K-value |
Ki=PPisat |
| Partial pressure relation of binary system |
P=yaP+ybP=xaPasat+(1−xa)Pbsat |
| Vapor phase composition of binary system |
ya=xaPasat+(1−xa)PbsatxaPasat |
| Partial pressure relation of multicomponent system |
P=∑yiP=∑xiPisat |
| Vapor phase composition of multicomponent system |
yi=∑xiPisatxiPisat |
| Description |
Equations |
Nonideal liquid solution
★ Ideal gas φ^iv=1
★ Lewis/Randall ref state fi∘=fi=Pisat |
yiP=xiγiPisat |
| Partial pressure relation of binary system |
P=yaP+ybP=xaγaPasat+(1−xa)γbPbsat |
| Vapor phase composition of binary system |
ya=xaγaPasat+(1−xa)γbPbsatxaγaPasat |
| Partial pressure relation of multicomponent system |
P=∑yiP=∑xiγiPisat |
| Vapor phase composition of multicomponent system |
yi=∑xiγiPisatxiγiPisat |
| Description |
Equations |
| Azeotrope |
xi=yi |
| Azeotrope equilibrium consition |
P=γiPisat |
| Activity coefficient from azeotrope |
γi=PisatP |
| Activity coefficient ratio from azeotrope |
γbγa=PasatPbsat |
| Description |
Equations |
| Least square objective function based on pressure |
fP=∑(P−Pcalc)i2 |
| Least square objective function based on excess Gibbs energy |
fgE=∑(gE−gcalcE)i2 |
| Least square objective function based on activity coefficient for binary system |
fγ=∑[(γaγa−γacalc)2−(γbγb−γbcalc)2]i |
|
|
Ideal gas |
Nonideal gas |
| Ideal liquid |
Solute a |
yaP=xaHa |
yaφaP=xaHaexp[∫P0PRTVa∞dP] |
|
Solvent b |
ybP=xbPbsat |
ybφ^bP=xbφbsatPbsatexp[∫PbsatPRTvbldP] |
| Nonideal liquid |
Solute a |
yaP=xaγaHHa |
yaφaP=xaγaHHaexp[∫P0PRTVa∞dP] |
|
Solvent b |
ybP=xbγbPbsat |
ybφ^bP=xbγbφbsatPbsatexp[∫PbsatPRTvbldP] |
| Description |
Equations |
| Mixing rule for Henry’s constant |
lnHa=j∑xilnHa,j |
| Description |
Equations |
| General LLE condition |
f^iαxiαγiα=f^iβ=xiβγiβ |
Compositions xaα,xbα,xaβ,xbβ
★ Two-suffix Margules equation |
xaαexp[RTA(xbα)2]xbαexp[RTA(xaα)2]xaα+xbαxaβ+xbβ=xaβexp[RTA(xbβ)2]=xbβexp[RTA(xaβ)2]=1=1 |
| Genral criteria for instability (separation) |
(∂xa2∂g2)T,P<0 |
Criteria for instability (separation)
★ Two-suffix Margules equation |
xaxbRT<2A |
Upper consolute temperature
★ Two-suffix Margules equation |
Tu=2RA |
| Description |
Equations |
| General VLLE condition |
f^iv=f^iα=f^iβ |
Composition and state variables xaα,xbα,xaβ,xbβ,ya,yb,T,P
★ Two-suffix Margules equation |
yaP=xaαexp[RTA(xbα)2]PasatybP=xbαexp[RTA(xaα)2]Pbsatya+ybxaα+xbαxaβ+xbβ=xaβexp[RTA(xbβ)2]Pasat=xbβexp[RTA(xaβ)2]Pbsat=1=1=1 |
| Description |
Equations |
| General SLE condition |
f^isXiΓifisfs=f^il=xiγifil=xiγifil |
Composition of SLE
★ Pure solid |
ln[xiγi]=RΔhfus,Tm[T1−Tm1]−R1∫TmTTΔcPsldT+RT1∫TmTΔcPsldT |
Composition of SLE
★ Pure solid.
★ Constant ΔcPsl |
ln[xiγi]=RΔhfus,Tm[T1−Tm1]−RΔcPsl[1−TTm−ln(TmT)] |
Composition of SLE
★ Solid solution |
ln[XiΓixiγi]=RΔhfus,Tm[T1−Tm1]−R1∫TmTTΔcPsldT+RT1∫TmTΔcPsldT |
Composition of SLE
★ Solid solution.
★ Constant ΔcPsl |
ln[XiΓixiγi]=RΔhfus,Tm[T1−Tm1]−RΔcPsl[1−TTm−ln(TmT)] |
| Description |
Equations |
Boiling point elevation
★ Solvent a, solute b |
T−Tboil=ΔhvapRTboil2γaxb |
| Activity coefficient from boiling point elevation data |
γb=RTboil2xb(T−Tboil)Δhvap |
Freezing point depression
★ Solvent a, solute b |
T−Tm=ΔhfusRTm2γaxb |
| Activity coefficient from freezing point depression data |
γb=RTm2xb(T−Tm)Δhfus |
| Osmotic pressure |
Π=−vaRTln(xaγa) |
Osmotic pressure
★ Ideal solution, dilute b |
Π=−vaRTxb |
| Molar mass from osmotic pressure data |
Mb=ΠRTCb |
| Description |
Equations |
| Chemical reaction expressed in stoichiometric coefficients |
∑νiAi |
| Extent of reaction |
dξ=νidni |
| Moles of species |
ni=ni∘+νiξ |
| Chemical equilibrium condition |
dξdG=0=∑μiνi |
| Gibbs energy of reaction |
Δgrxn∘=∑νigi∘ |
| Equilibrium constant |
K=∏(fi∘f^i)νi |
| Equilibrium constant and Gibbs energy of reaction |
lnK=−RTΔgrxn∘ |
| Description |
Equations |
| Gibbs energy of formation method |
Δgrxn∘=∑νiΔgf,i∘ |
| T dependence of K |
dTdlnK=RT2Δhrxn∘ |
T dependence of K
★ Constant Δhrxn∘ |
ln(K2K1)=−RΔhrxn∘(T21−T11) |
T dependence of K
★ Δhrxn∘(T) |
ln(K2K1)=−RΔhrxn∘(T21−T11)+∫T1T2RT2∫T1T∑νicP,idTdT |
| Description |
Equations |
| General expression |
K=∏(fi∘yiφ^iP)νi |
| Lewis fugacity rule |
K=Pν∏(yiφi)νi |
| Ideal gas |
K=Pν∏(yi)νi |
| Description |
Equations |
| General expression |
K=∏(fi∘xiγifi)νi |
| Low pressure, neglegible pressure dependence |
K=Pν∏(xiγi)νi |
| Ideal solution |
K=Pν∏(xi)νi |
| Description |
Equations |
| General expression |
K=∏(fi∘XiΓifi)νi |
| Low pressure, neglegible pressure dependence |
K=Pν∏(XiΓi)νi |
| Ideal solid solution |
K=Pν∏(Xi)νi |
| Description |
Equations |
| Chemical reactions expressed in stoichiometric coefficients |
k=1∑Ri=1∑mνk,iAi |
| Moles of species |
ni=ni∘+∑k=1Rνk,iξ |
| Description |
Equations |
| Gibbs energy and non-Pv work |
δW∗≥(dG)T,P |
| Gibbs energy of reaction and reversible work |
W=ΔG=zξFE |
| Nerst equation |
E=Erxn∘−zFRTln[vap∏(Pi)νiliq∏(biγi)νi] |
| Standard Gibbs energy of reaction |
Δgrxn∘=−zFErxn∘ |
| Standard potential of reaction |
Erxn∘=−zFΔgrxn∘ |
| Standard potential of reaction |
Erxn∘=Ered∘(cathode)−Ered∘(anode) |
| Average activity coefficient |
XXa YXbaXX(z+)++bYX(z−)−γ±=(γ+aγ−b)1/(a+b) |
| Average activity coefficient |
XYXX++YX−γ±=γ+γ− |
| Debye-Huckel model |
lnγ±=−A∣z+z−∣I |
| Ionic strength |
I=21∑zi2bi |